Chemistry, the study of matter and its properties, encompasses a wide array of substances with diverse characteristics. Among these are chemicals with a pH greater than seven, commonly referred to as alkaline substances. Understanding the properties, applications, and environmental impacts of chemicals with pH greater than seven is crucial in various industries. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the fundamentals of alkaline chemicals, their significance, and their role in shaping our world.
Understanding pH and Alkalinity
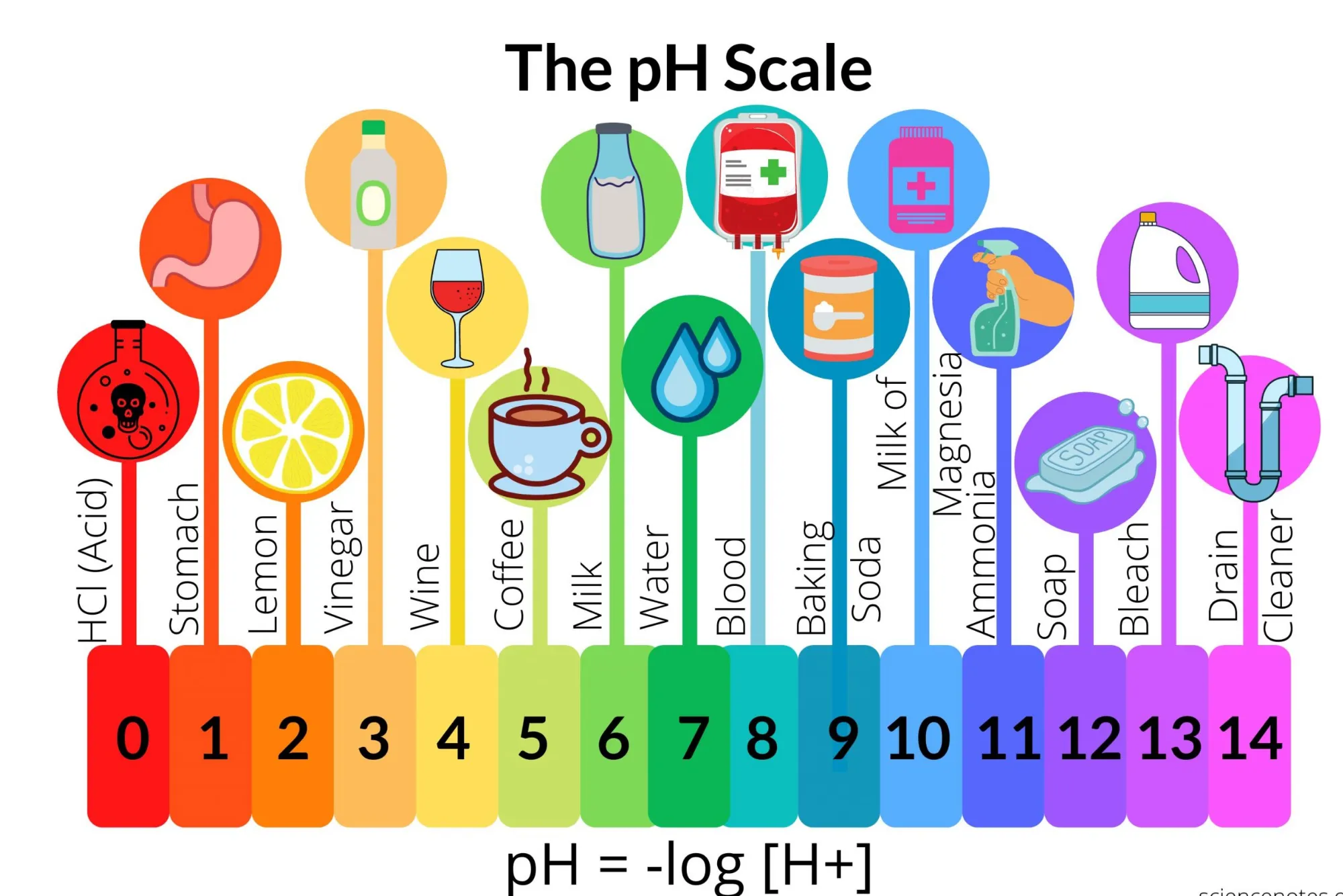
The pH scale is a logarithmic scale ranging from 0 to 14, used to measure the acidity or alkalinity of a substance. A pH of 7 is considered neutral, while pH values less than 7 indicate acidity, and pH values greater than 7 indicate alkalinity. Alkaline chemicals, also known as bases, have pH values greater than 7. They exhibit unique properties that differentiate them from acidic or neutral substances.
Properties of Alkaline Chemicals
Alkaline chemicals possess several distinctive properties that make them essential in various applications:
Neutralization: One of the most notable properties of alkaline chemicals is their ability to neutralize acids. When an acidic substance is combined with an alkaline substance, they react to form water and a salt, effectively neutralizing the acidic properties.
Corrosion: While alkaline substances are generally less corrosive than acidic substances, they can still corrode certain materials, especially metals. Proper handling and storage are necessary to prevent damage to equipment and infrastructure.
Solubility: Many alkaline chemicals are highly soluble in water, facilitating their use in aqueous solutions and making them effective for applications such as cleaning and water treatment.
Detergency: Alkaline chemicals are often used as detergents due to their ability to break down grease and oils. They are commonly found in household cleaning products, industrial degreasers, and laundry detergents.
Applications of Alkaline Chemicals
The versatility of alkaline chemicals lends them to a wide range of applications across various industries:
Industrial Processes: Alkaline chemicals play a crucial role in numerous industrial processes, including metal cleaning, wastewater treatment, and chemical synthesis. They are used to adjust pH levels, neutralize acidic byproducts, and facilitate chemical reactions.
Agriculture: In agriculture, alkaline chemicals are utilized to adjust soil pH and improve soil fertility. By raising the pH of acidic soils, these substances enhance nutrient availability and promote healthy plant growth.
Water Treatment: The purification of water for drinking, irrigation, and industrial use relies on alkaline chemicals to adjust pH levels and remove contaminants. They help ensure safe and clean water for various applications.
Construction: Alkaline chemical are integral to the production of construction materials such as cement and concrete. They contribute to the setting process, improve durability, and enhance the performance of these materials in diverse environmental conditions.
Pharmaceuticals: In the pharmaceutical industry, alkaline chemicals are used in drug formulation and synthesis processes. They play a crucial role in controlling pH levels, stabilizing active ingredients, and ensuring the efficacy and safety of medications.
Environmental Considerations
While alkaline chemicals offer numerous benefits across industries, their usage can have environmental implications:
Wastewater Discharge: Industries that utilize alkaline chemicals in their processes may discharge wastewater containing elevated pH levels. If not properly treated, this wastewater can have detrimental effects on aquatic ecosystems, leading to habitat degradation and harm to aquatic organisms.
Soil Contamination: Improper disposal of alkaline substances can lead to soil contamination, affecting soil pH and nutrient levels. This can have adverse effects on plant growth and soil health, impacting agricultural productivity and ecosystem integrity.global fluorine chemical llc.
Air Pollution: Some alkaline chemicals, particularly those used in industrial processes, may emit volatile compounds into the atmosphere, contributing to air pollution and respiratory health issues in nearby communities.
Sustainable Practices and Solutions
Addressing the environmental impacts of alkaline chemical usage requires a concerted effort from industries, regulators, and communities:
Waste Management: Implementing effective waste management practices, such as onsite treatment and recycling, can minimize the discharge of alkaline wastewater into natural water bodies.
Green Chemistry: Embracing green chemistry principles can lead to the development of safer and more sustainable alternatives to traditional alkaline chemicals. These alternatives are designed to minimize environmental impact while maintaining effectiveness in various applications.
Regulatory Compliance: Adherence to environmental regulations and standards is essential for industries utilizing alkaline chemicals. Compliance with discharge limits, pollution prevention measures, and reporting requirements helps mitigate environmental risks and protect ecosystems.
Chemicals with a pH greater than seven, or alkaline chemicals, play a vital role in numerous industries, from manufacturing and agriculture to healthcare and construction. Understanding their properties, applications, and environmental impacts is essential for responsible usage and sustainable development. By adopting sustainable practices, embracing innovation, and prioritizing environmental stewardship, we can harness the benefits of alkaline chemicals while minimizing their adverse effects on the environment.